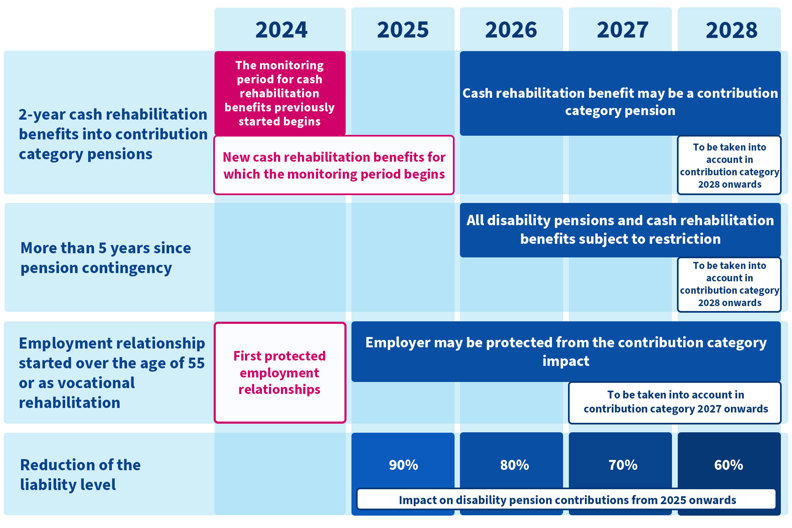
The employer's liability level decreases to 60% from the previous level
The employer's liability level will be gradually decreased to 60% from the previous level. The liability level will be decreased by 10% annually between 2025 and 2028. In 2028, the liability level can be no more than 60%.
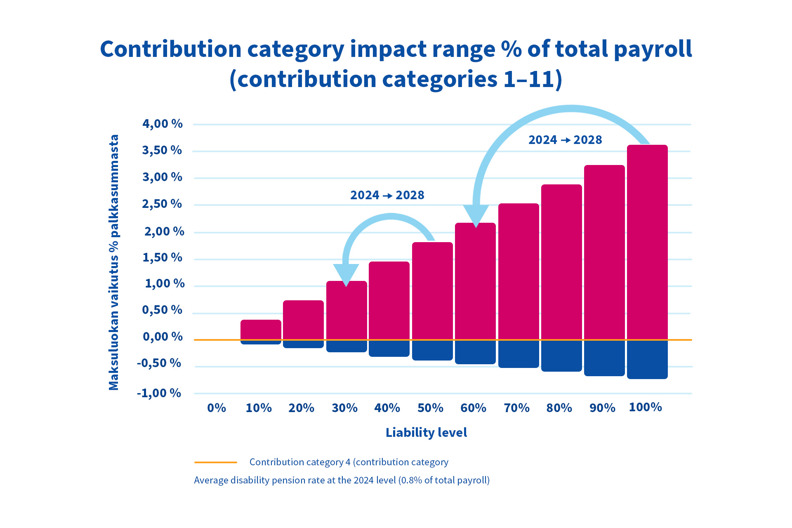
The decrease in the liability level applies to all employers with liability. If an employer's liability level was previously 100%, it will be 60% in 2028. If the liability level was previously 50%, it will be 30% in 2028. When the liability level decreases, the contribution category impact decreases. Going forward, a smaller portion of the disability pension contribution will be determined by the contribution category.
If the employer's contribution category is high (above 4), the contribution increments will decrease, and the insurance contribution will decrease. Correspondingly, if the employer's contribution category is low (below 4), the contribution reductions will decrease, and the insurance contribution will increase.